Ibaraki Prefecture
| Ibaraki Prefecture | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| Capital | Mito | ||||||||
| Region | Kantō | ||||||||
| Island | Honshū | ||||||||
| Governor | Masaru Hashimoto | ||||||||
| Area (rank) | 6,095.58 km² (23rd) | ||||||||
| - % water | 4.8% | ||||||||
| Population (October 1, 2000) | |||||||||
| - Population | 2,985,424 (11th) | ||||||||
| - Density | 490 /km² | ||||||||
| Districts | 7 | ||||||||
| Municipalities | 43 | ||||||||
| ISO 3166-2 | JP-08 | ||||||||
| Website | www.pref.ibaraki.jp/bukyoku/seikan/kokuko/en | ||||||||
| Prefectural symbols | |||||||||
| - Flower | Rose (Rosa) | ||||||||
| - Tree | Ume tree (Prunus mume) | ||||||||
| - Bird | Eurasian Skylark (Alauda arvensis) | ||||||||
| - Fish | {{{Fish}}} | ||||||||
 Symbol of Ibaraki Prefecture |
|||||||||
| Template ■ Discussion ■ WikiProject Japan | |||||||||
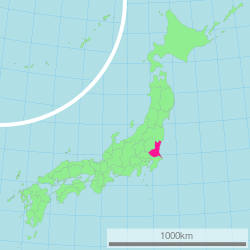
Ibaraki Prefecture (茨城県 Ibaraki-ken) is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region on Honshū island. The capital is Mito.
Contents |
History
Ibaraki Prefecture was previously known as Hitachi Province. In 1871, the name of the province became Ibaraki. The name is also occasionally pronounced "Ibaragi" by those outside of the prefecture.
Geography
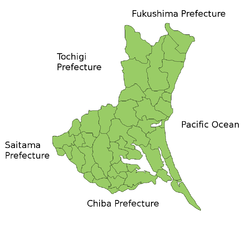
Ibaraki Prefecture is the northeastern part of the Kantō region, stretching between Tochigi Prefecture and the Pacific Ocean and bounded on the north and south by Fukushima Prefecture and Chiba Prefecture. It also has borders on the southwest with Gunma Prefecture and Saitama Prefecture. The northernmost part of the prefecture is mountainous, but most of the prefecture is a flat plain with many lakes.
Cities
Thirty-two cities are located in Ibaraki Prefecture:
|
|
|
Towns and villages
Towns and villages in each district:
|
|
|
Mergers
Future mergers
Economy
Ibaraki's industries include energy, particularly nuclear energy, production, as well as chemical and precision machining industries. The Hitachi company was founded in the Ibaraki city of the same name.
Demographics
Ibaraki's population is increasing modestly as the Greater Tokyo region spreads out.
Culture
Ibaraki is known for natto, or fermented soybeans, in Mito, watermelons in Kyōwa (recently merged into Chikusei), and chestnuts in the Nishiibaraki region.
Ibaraki is famous for the martial art of Aikido founded by Ueshiba Morihei, also known as Osensei. Ueshiba spent the latter part of his life in the town of Iwama, now part of Kasama, and the Aiki Shrine and dojo he created still remain.
There are castle ruins in many cities, including Mito, Kasama, and Yūki.
Kasama is famous for Shinto and art culture and pottery.
The capital Mito is home to Kairakuen, one of Japan's three most celebrated gardens, and famous for its over 3,000 Japanese plum trees of over 100 varieties.
Sports
The sports teams listed below are based in Ibaraki.
Football (soccer)
- Kashima Antlers (Kashima)
- Mito HollyHock (Mito)
- Ryutsu Keizai University F.C. (Ryūgasaki)
Volleyball
- Hitachi Sawa Rivale (Hitachinaka)
Rugby
- Kashima Rugby Football Club RFC
Tourism
- Kairakuen Park
- Mount Tsukuba
- Kashima Shrine
Transportation and access
Railways
- East Japan Railway Company
- Jōban Line
- Utsunomiya Line (Tōhoku Main Line)
- Mito Line
- Suigun Line
- Kashima Line
- Tōhoku Shinkansen
Prefectural symbols
Pronunciation
The prefecture is often mispronounced "Ibaragi". However, the correct pronunciation is "Ibaraki." According to the author of "Not Ibaragi, Ibaraki" (いばらぎじゃなくていばらき ibaragi ja nakute ibaraki) [1], this is most likely due to a mishearing of the softening of the 'k' sound in Ibaraki dialect.
References
External links
- Official Ibaraki Prefecture homepage
- The E-Ibaraki Report: articles and commentary of foreigners living in Ibaraki, produced by the International Affairs Division, Ibaraki Prefecture
- Ibaraki Japan
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||